There is hardly a subject of the German is currently as strong as the rising Rents. Because almost every Second person lives in Germany for rent. An Overview of the current debate, problems and solution approaches.

The anger about higher and higher rental rates has pushed this spring, tens of thousands to Protest on the streets of Germany. Whether or not Rent control, the Rent ceilings, compulsory purchase claims, to curtail the Power of the landlords, to be in the whole country according to the. According to a new survey, commissioned by the parliamentary group of the left party in order to hire the Inventory (no new leases) in the last five years nationwide, 11.4 percent.
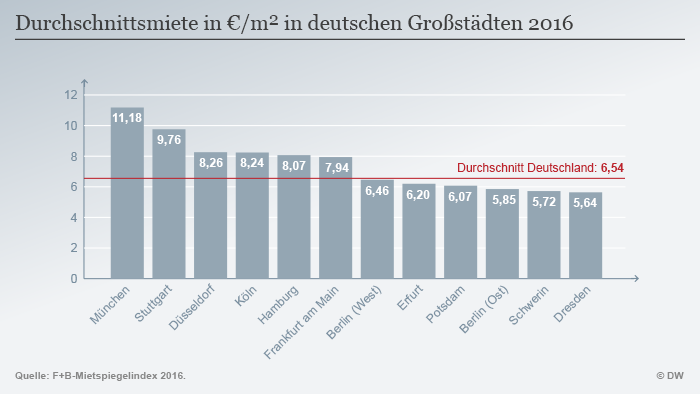
Where the Rent is particularly high?
Absolute front-runner in the square meter prices in Munich. There is a square meter of living space costs an average of almost 18 Euro. In Frankfurt am Main with € 14.20 per square meter, and at Position three of Stuttgart, just under 14 euros per square meter. In Berlin, the average net cold rent according to Rent index in 2019, per square meter at around 6,72 Euro. The cheapest rent there was in North Rhine-Westphalia, Warstein, with 4.64 Euro per square meter.
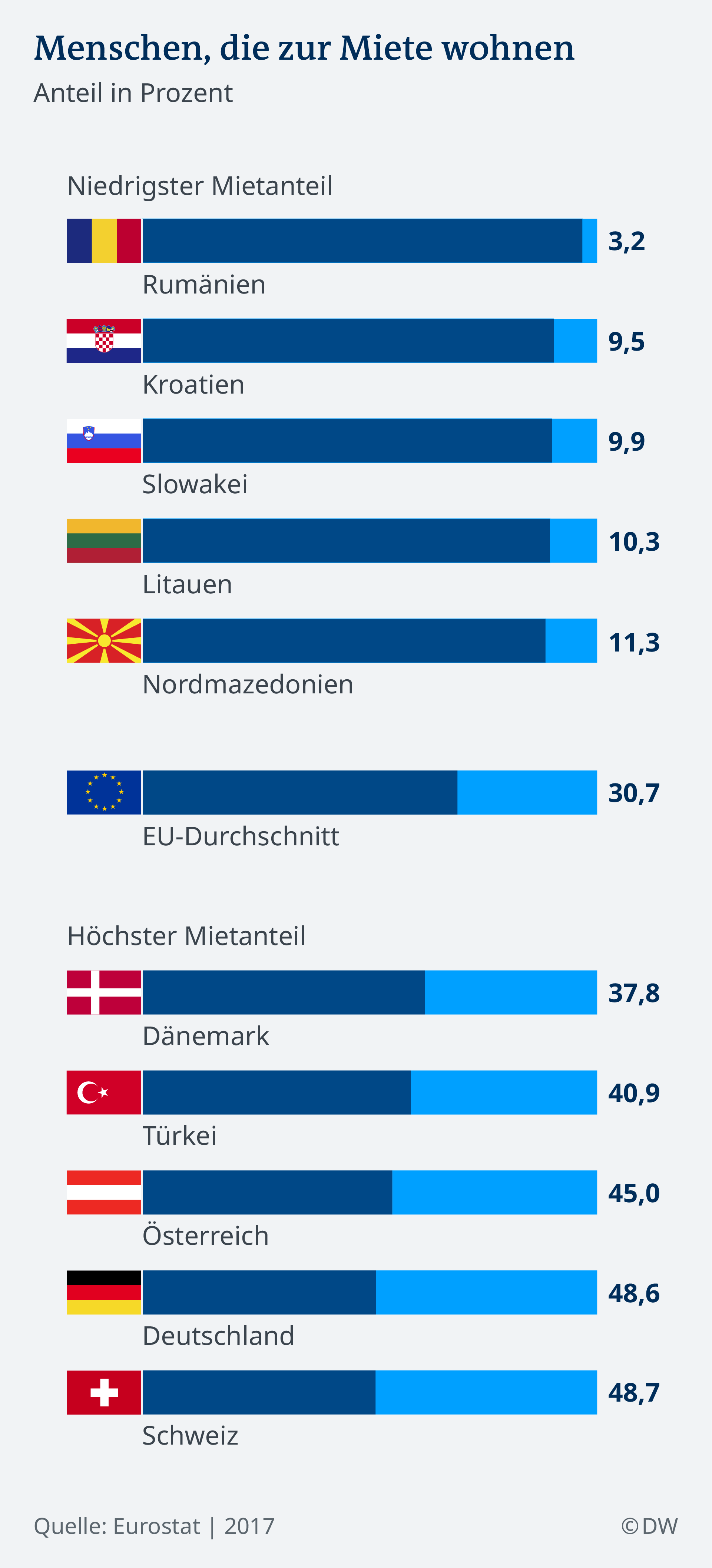
Why is cheaper Leased nearly?
Many formerly public apartments, are now in the hands of corporations. For example, the city of Dresden in 2006, and sold as the first German municipality of their entire housing stock, and repayments on your debt in the amount of 741 million euros.
Vonovia, the largest housing company in Germany, managed more than 300,000 homes. One of its objectives is “to implement steady rent increases a yield, which is then given to the share holder. For the apartment itself, again, is not at all relevant, but only the rate of return,” says Susanne Heeg is a Professor of Geographical urban research at the Goethe University in Frankfurt am Main.
Another reason for the price spiral, there is a growing demand and the consequent shortage of supply in the centre of attractive cities is. “Almost half of a year at University, and studied not in the country, but in towns and cities. It is clear, therefore, that cities attract young people,” says Heeg. Who could afford to stay after graduation in the cities.
Instruments with which the Grand coalition is not responding?
1.5 million – So many apartments want the Federal government until the end of the current term, i.e. by 2021, create. The CDU/CSU and SPD in their coalition agreement. Part of it will be social housing – for the construction of the countries, however, are actually responsible. Nevertheless, the Federal government contributes EUR 1.5 billion per year on social housing. Overall, the housing, so New social housing should be funded in this term of five billion euros.
Criticism: in Order to create social housing, the government and private construction projects. In return, may low living wage in a so-called certificate of eligibility for a specified period of time there particularly favorable. The Problem: The mietober limit for social housing will not be available forever. After a certain period of time, you fall out of the rental bond – 2018 that was true of almost 49.000 apartments. This means, then the Rent will also increase in these cheap apartments. And there is still another Problem: last year almost 27,000 publicly funded were built, social housing. The tenants Association estimates that annually 80.00 have to be built to meet demand.
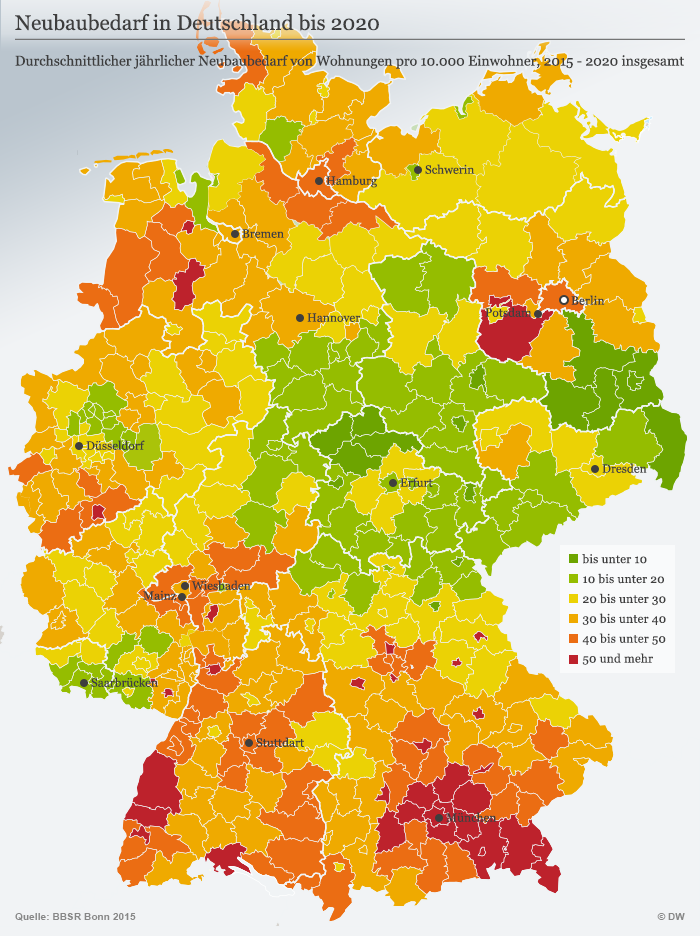
The German tenants ‘ Association (DMB) requires that annually, 80,000 are socially constructed dwellings and 120,000 affordable rental apartments. Tax incentives for builders should be bound to relevant upper limits. In fact, much of the newly-built is expensive ownership and rental housing, criticized the tenants ‘ Association. Overall, the construction of new housing demand, around 25 per cent behind the actual apartment and the objectives of the Federal government is retarded.
The rental price brake Since the summer of 2015 in Germany is a brake on Rent prices. The Grand coalition has tightened up to the beginning of the year once again. Now the rent may not be in the case of new contracts, more than ten percent of the “local comparative rent”.
Review: Rent control only applies to “areas with difficult housing market”. Where is the lie, choose the länder. And there are many exceptions in the case of Rent control: do not apply in the case of new buildings, renovations, or if the rent of the previous tenant was already higher.
Since Rent control applies only to new lettings, the Rich benefited from your also, anyway, only, is Volker Eichener, Professor of political science at the University of Düsseldorf, to bear in mind. “The landlord can pick and choose the prospective tenants, appearing to him as the best risks.” Therefore, officials couples were more likely to receive the award as workers or students, so Eichener.
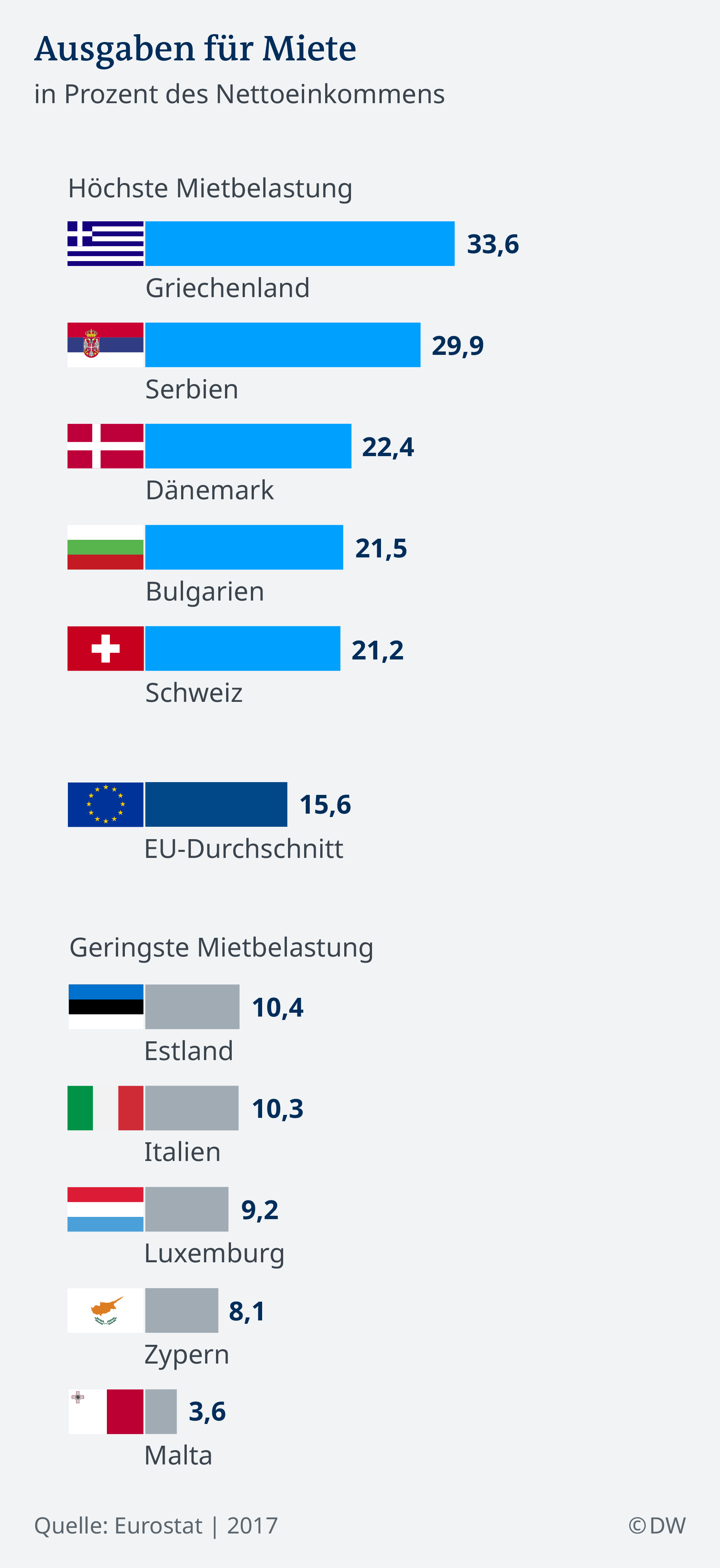
Housing benefit – From 2020 onwards, a new living is to relieve the money low-income earners in the rent. About 660,000 households are set to benefit from this government subsidy. Every two years he should be on the overall development of Rents and income adjusted. However, you must still agree to the Federal Council, because the living benefit will be paid half each by the Federal and the länder.
Criticism: social associations and unions in the Reform is a right step, but criticise the fact that the problems of scarce housing and rising Rents is not to be solved. Tenants of the Federal government, the Green party and the left party miss schemes, which allow for grants at higher Rent in energetically modernized buildings.

In April tens of thousands against high Rents demonstrated in Berlin
What ideas are there?
Expropriation – this week, on 14. June, want to pass in a Berlin citizens ‘ initiative to the Senate signatures for a referendum for the expropriation of large housing corporations. Expropriation of some legal but highly controversial. Also, the public sector would have to pay the housing corporations billions in compensation. Also the tenants ‘ Association is skeptical. Expropriations continued, so that won’t help the housing market at the moment, so DMB President Franz-Georg Rips.
Mietdeckel – The Senate could soon decide to stop all rent increases for the next five years. The left party also calls for nationwide. In Berlin, however, the shot could backfire: The Association of Owners house and has called all the landlords to increase Rents as quickly as possible before the impending Mietdeckelung yet.
Ban on advertising – Federal Minister of justice Katarina Barley (SPD) wants to ban landlords in the future to advertise for homes with inflated rental prices. Critics would say that such a ban does not create new housing.
New method for building land and construction – in General, the public sector should not sell their land, but housing companies only lease, calls for the German tenants ‘ Association. So the investors would have to Finance any property purchase more and might be cheaper to build. This could be rented in consequence of the apartments cheaper. The German Association of cities appealed to the Federal government, the Länder and the local authorities to speed up the Build by regulations to be simplified and slimmed down.









