The Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 is intended to enable smaller and more energy-efficient AR glasses that users can wear for several hours at a time. While previous solutions were designed for AR, VR and MR, the new platform is dedicated exclusively to augmented reality. Several well-known OEMs are developing AR glasses based on the new solution.
So far, the focus at Qualcomm has been on the development of so-called XR solutions, i.e. platforms that can be used for AR (Augmented Reality), VR (Virtual Reality) and MR (Mixed Reality). In the premium segment, for example, Snapdragon XR2 Gen 1 and XR2+ Gen 1 are offered, which are in the Meta Quest 2 and Quest Pro, while the upper class is served by the Snapdragon XR1 Gen 1.
New platform for AR only
At the Snapdragon Tech Summit, Qualcomm presented the Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1, a platform designed exclusively for augmented reality. The solution covers the highest premium segment, but Qualcomm is planning further gradations for lower performance and price ranges. The company has already won Lenovo, LG, Nreal, Oppo, Pico, Qoonoq, Sharp, TCL, Tencent, Vuzix and Xiaomi for the Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1.
-
 Qualcomm Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 (Image: Qualcomm)
Qualcomm Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 (Image: Qualcomm)
Figure 1 of 4
 Qualcomm Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 (Image: Qualcomm)
Qualcomm Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 (Image: Qualcomm) Qualcomm Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 (Image: Qualcomm)
Qualcomm Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 (Image: Qualcomm) The portoflio for XR and AR platforms (Image: Qualcomm)
The portoflio for XR and AR platforms (Image: Qualcomm)The platform aims to enable manufacturers to design AR glasses for consumers and companies that can be worn for an extended period of time without symptoms of fatigue. “You want to wear these AR glasses all day,” said a company spokesman in the run-up to the in-house exhibition currently taking place in the USA. This statement is undecided, but Qualcomm has taken numerous measures to get closer to this goal.
Complex calculations take place on the host< /h2>
Above all, the Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1 should enable significantly smaller, lighter and particularly efficient and thus energy-saving AR glasses. Qualcomm states a consumption of less than 1 watt for the new platform. Strictly speaking, the solution developed from scratch consists of three processors in the AR glasses and an external host for complex calculations. An AR and AR co-processor and a chip for connectivity are used in the glasses for so-called “on-glass processing”. Complex calculations take place on the wirelessly connected host, which can be a Snapdragon smartphone, Snapdragon PC, or other compatible device such as a “puck” like the Magic Leap.
-
 Complex calculations take place on the host (image: Qualcomm)
Complex calculations take place on the host (image: Qualcomm)
Image 1 of 6
 4nm AR processor (Image: Qualcomm )
4nm AR processor (Image: Qualcomm )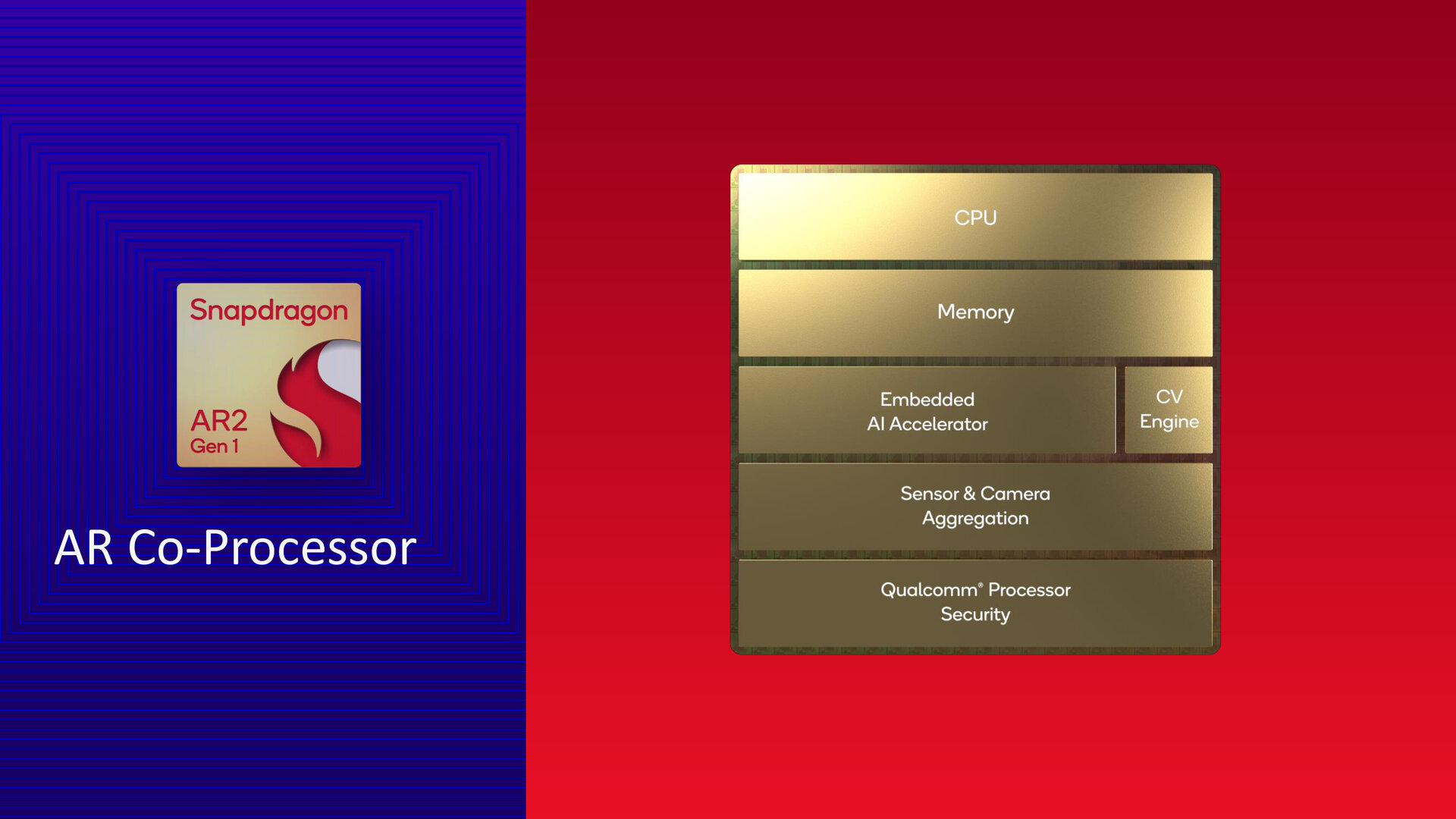 AR co-processor (Image: Qualcomm)
AR co-processor (Image: Qualcomm) AR processor im Eyeglass temples (Image: Qualcomm)
AR processor im Eyeglass temples (Image: Qualcomm) AR co-processor above the nose bridge (Image: Qualcomm)
AR co-processor above the nose bridge (Image: Qualcomm) FastConnect 7800 (Image: Qualcomm)
FastConnect 7800 (Image: Qualcomm)Qualcomm has the AR processor manufactured in 4 nm and accommodates function blocks in it, for example for processing the data from up to nine cameras running simultaneously. The AR processor is also responsible for motion detection and localization of the user in space, hand tracking and 6 DoF freedom of movement and offers a reflection engine. The AR co-processor handles eye tracking and iris authentication to support features like foveated rendering to restrict workloads to the area the user is viewing, which in turn should benefit power consumption. The FastConnect 7800, a chip prepared for Wi-Fi 7 and designed to enable latencies of less than 2 ms between AR glasses and the host, ensures connectivity.
Distributed chips for more compact design
The background to the division into several chips is a more compact design for future AR glasses that Qualcomm is aiming for, which can do with reduced wiring and no longer concentrate waste heat on one point. The PCB for the main processor can be 40 percent smaller, the company explains, citing the chip's dimensions as 12 × 10 mm. The AR co-processor is 6.2 × 4.2 mm. While the AR processor fits into one of the temples and the chip for connectivity is accommodated in the other, the AR co-processor sits above the nose bridge. Among other things, this structure should simplify the connection of the cameras and reduce the number and length of the cables. With the Snapdragon AR2 Gen 1, AR glasses should finally be created in a “stylish form factor”, says the manufacturer.
 Reduced main processor size (Image: Qualcomm)
Reduced main processor size (Image: Qualcomm)ComputerBase has information about this article from Qualcomm received under NDA in advance and at a manufacturer event in Maui, Hawaii. Travel, departure and hotel expenses were borne by Qualcomm. There was no influence on the part of the manufacturer or an obligation to report. The only requirement was the earliest possible publication date.