With the Crucial P5 Plus, the Micron brand makes its PCIe 4.0 debut two years after the competition and the connection to the upper class of M.2 SSDs for consumers: the model is presented strong in the test, there is no real weakness. Even the temperature is only an issue in extreme situations without a cooler.
Table of contents
- 1 With PCIe 4.0 debut the connection to the top of the SSD succeeds
- The late change to PCIe 4.0
- Micron's 176-layer NAND with new architecture
- Features and prices at a glance
- 2 benchmarks, cache analysis and temperatures
- Test system and test methodology
- Cache analysis (SLC mode)
< li> Copy processes in Explorer
- Consistency of performance in PCMark 10
- CrystalDiskMark
- Temperatures over time
- The PCIe 4.0 debut succeeds
The late change to PCIe 4.0
Whether Samsung, Western Digital or the numerous SSD third-party providers: Almost all manufacturers have long had at least one SSD with the current PCIe 4.0 interface in their range. Micron is therefore a late bloomer in this regard, because only recently the first step was made with the OEM SSD Micron 3400 to PCIe 4.0 and today follows with the P5 Plus, the first retail SSD from the brand subsidiary Crucial, which uses the new interface.
The surprise spoiled by an online retailer who had already unveiled the Crucial P5 Plus in advance. The older Crucial P5 (test) will be discontinued (EOL) later this year, Crucial explained. The P5 Plus will replace this in the medium term.
Another controller of your own
It is conceivable that it took Micron a while to get its own controller technology ready for PCIe 4.0. Using an external solution like Phison E16 or Phison E18 was apparently not an option. And so a proprietary Micron controller is now used, about which little information is available apart from the identification DM02A1. Crucial has confirmed, at least when asked, that the controller has eight NAND channels, which is also common with consumer SSDs in the upper performance class. The expiring P5 series is equipped with the DM01B2.
-
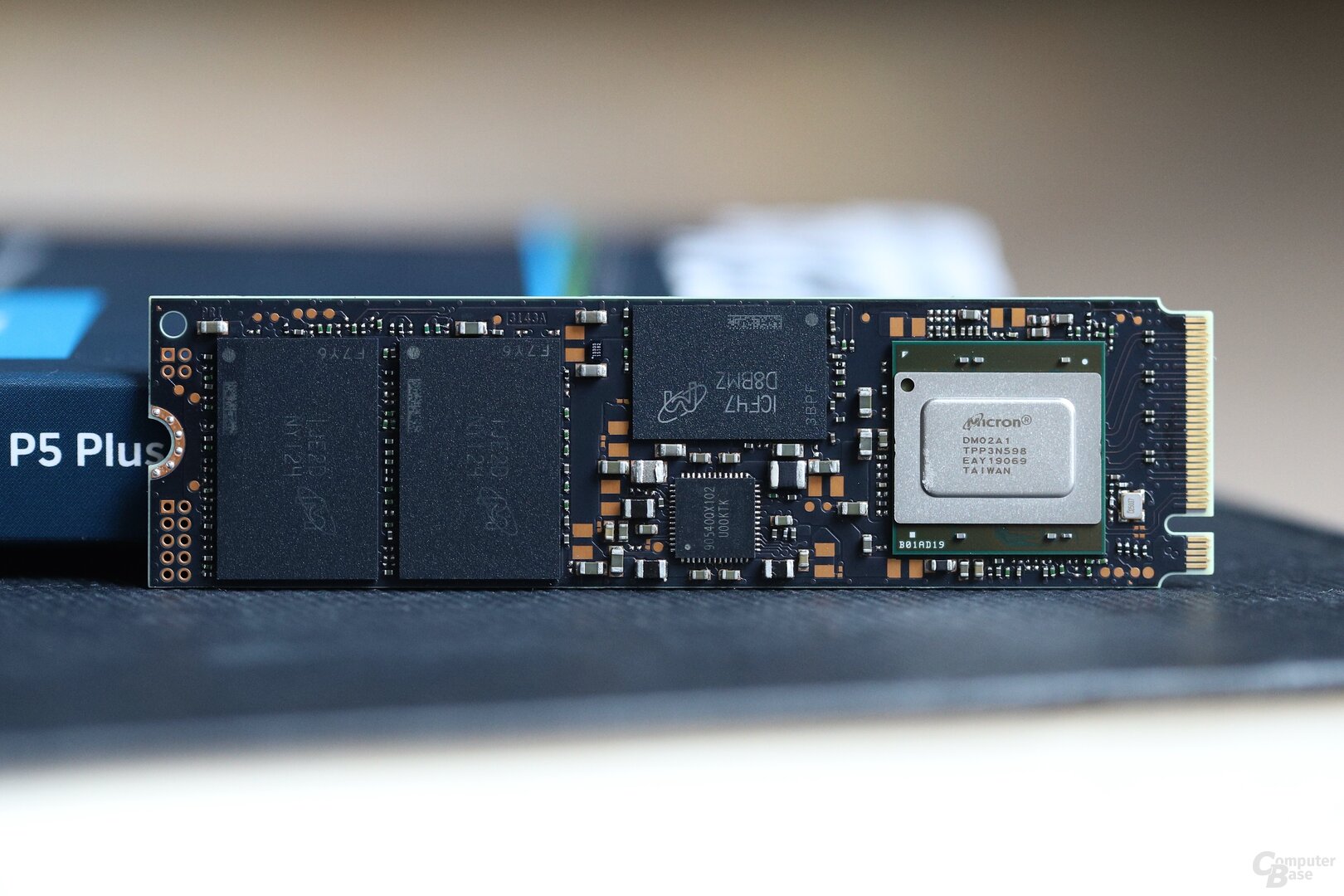 Crucial P5 Plus SSD with PCIe 4.0
Crucial P5 Plus SSD with PCIe 4.0
Image 1 of 3
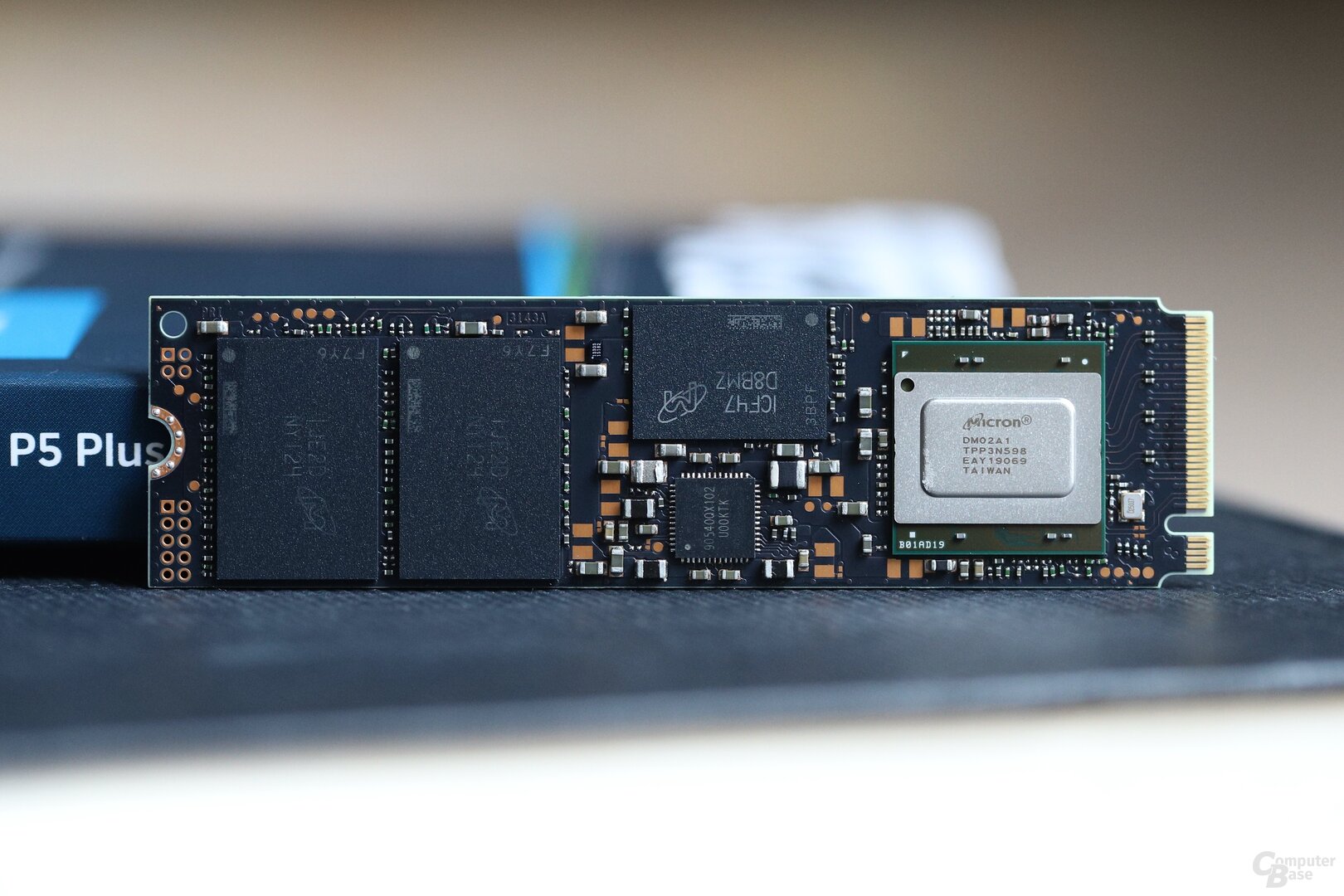 Crucial P5 Plus SSD with PCIe 4.0
Crucial P5 Plus SSD with PCIe 4.0 < figure> 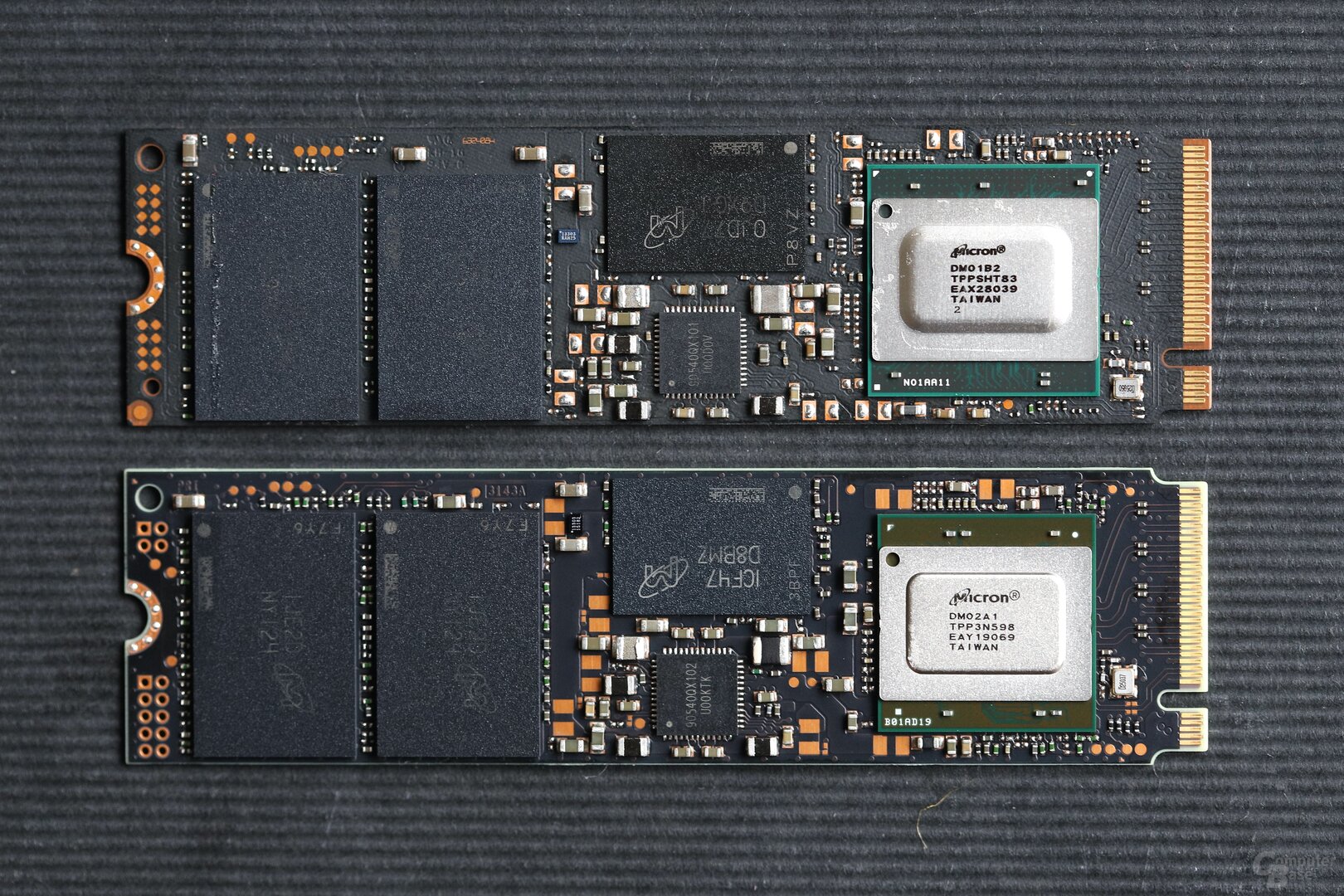 P5 above, P5 plus below
P5 above, P5 plus below
The Crucial P5 Plus is again available in M.2 format with a length of 80 mm and is offered with storage capacities of 500 GB, 1 TB and 2 TB. The editors were given the 1 TB version as a test sample.
Accelerated to 6,600 MB/s
Speaking of performance: the throughput rates increase significantly compared to the older Crucial P5 (test) with PCIe 3.0. Instead of up to 3,400 MB/s, there are now up to 6,600 MB/s in the data sheet, which, as always, applies to the maximum sequential read rate. At this point, other models such as Corsair MP600 Pro (test), Samsung 980 Pro (test) or WD Black SN850 (test) have already reached 7,000 MB/s. Some SSDs like the Patriot Viper VP4300 (test) even achieve almost 7,500 MB/s in benchmarks.
The sequential write rate in SLC mode also increases significantly with up to 5,000 MB/s for the P5 Plus compared to a maximum of 3,000 MB/s for the P5. With 4K random transfers, the P5 Plus also achieves significantly more with 720,000/700,000 IOPS when reading/writing.
Microns 176-Layer- NAND with new architecture
Since separating from the former joint venture partner Intel, Micron has been developing the 3D NAND on its own. Instead of relying on the floating gate principle (FG) continued by Intel, Micron made the change to the so-called replacement gate architecture (RG), which is closer to the charge trap flash design (CTF) from Samsung, SK Hynix and WD/Kioxia is located. First, the RG-NAND from Micron was applied in a small edition with 128 cell layers, which was more of a first step. The current Micron B47R generation uses 176 layers, which also represents the current maximum number of cell layers in the industry.
-
 Infographic on Microns 176-Layer-NAND (Image: Micron)
Infographic on Microns 176-Layer-NAND (Image: Micron)
Image 1 of 5
 Infographic on Micron's 176-Layer-NAND
Infographic on Micron's 176-Layer-NAND 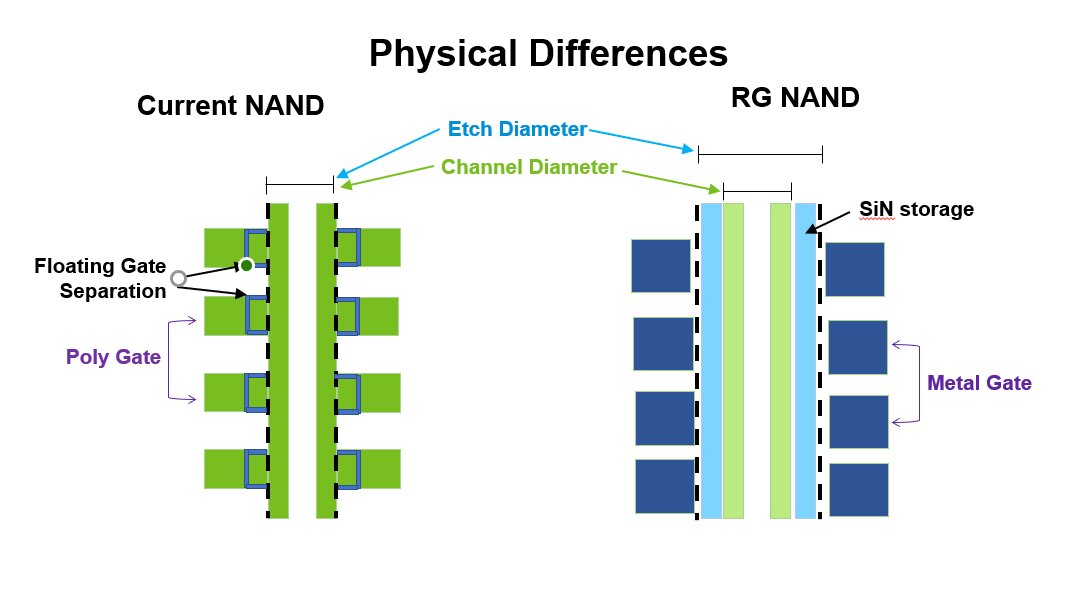 Floating Gate versus Replacement Gate
Floating Gate versus Replacement Gate  Microns 176-Layer-NAND
Microns 176-Layer-NAND Micron promises progress, especially in terms of storage density, but also in terms of performance. Read and write latency is said to have been reduced by more than 35 percent compared to the 96-layer generation and by more than 25 percent compared to the 128-layer generation. The NAND interface (ONFI) was accelerated from 1,200 to 1,600 MT/s and thus by a third.
SLC and DRAM cache
Like almost all current SSDs, the Crucial P5 Plus also uses an SLC cache to increase the write speed. The data is then initially written in SLC mode with only 1 bit per cell and only later permanently saved in TLC mode with 3 bits per cell. Once again Crucial relies on a dynamic SLC cache, the size of which depends on the free storage space. The TLC memory is then operated to a certain extent in SLC mode. According to Crucial, this is a maximum of around 10 percent of the storage capacity. This means that the models with 500 GB, 1 TB and 2 TB storage space have an SLC cache of 50 GB, 100 GB and 200 GB, respectively. In addition, the manufacturer provides information on the performance after the SLC cache when the data is written in the slower TLC mode.
According to Crucial, the DRAM cache (LPDDR4 from Micron) has a storage volume of 1 GB in the 500 GB and 1 TB variants, and 2 GB in the 2 TB model. The cache is used, among other things, for the mapping table as temporary storage; user data is not saved there. Since 1 GB DRAM per 1 TB NAND Flash is common, the 500 GB model is comparatively lavishly equipped with 1 GB.
Equipment and prices at a glance
Like its expiring predecessor, the Crucial P5 Plus does not have a heat sink. Data encryption according to TCG Opal 2.0 is supported. The manufacturer's guarantee covers the usual five years, but expires prematurely if previously defined write volumes, the so-called “Total Bytes Written” (TBW), are exceeded. With 300 TB, 600 TB and 1,200 TB, the TBW are exactly on the same level as the Crucial P5.
The market launch of the Crucial P5 Plus takes place with recommended prices of around 108 US dollars (500 GB), 180 US dollars (1 TB) and 368 US dollars (2 TB). The EIA for Germany was not yet available in advance. But in online retail it is becoming apparent that the euro prices will be at a similar level.
Crucial P5 Plus Crucial P5 Controller: Micron, 8 NAND-Channel Micron DM01B2, 8 NAND-Channel DRAM-Cache: 1,024 MB LPDDR4 Variant 2,048 MB LPDDR4? LPDDR4 memory capacity: 500/1,000/2,000 GB 250/500/1,000/2,000 GB Memory chips: Micron? ? TLC (3D, 176 layers) NAND,? Micron? ? TLC (3D, 96 layers) NAND,? Form factor: M.2 (80 mm) Interface: PCIe 4.0 x4 PCIe 3.0 x4 seq. Read: 6,600 MB/s 3,400 MB/s seq. Write: 3,600 MB/s Variant 5,000 MB/s 1,400 MB/s Variant 3,000 MB/s 4K Random Read: 360,000 IOPS variant 630,000 IOPS variant 720,000 IOPS 210,000 IOPS variant 390,000 IOPS variant 430,000 IOPS 4K Random Write: 100,000 IOPS variant 700,000 IOPS 355,000 IOPS variant 500,000 IOPS Power consumption activity (typ.):? Power consumption activity (max.):? Power consumption idle:? Power consumption DevSleep:? Power consumption L1.2:? Functions: NVMe, NCQ, TRIM, SMART, Garbage Collection Encryption: TCG Opal 2.0 AES 256, IEEE-1667, TCG Opal 2.0, Windows eDrive Total Bytes Written (TBW): 300 terabyte variant 600 terabyte variant 1,200 terabyte 150 terabyte variant 300 terabyte variant 600 terabyte variant Guarantee: 5 years Price: – from € 47/from € 59/from € 132/from € 240 Price per GB: – € 0.19/€ 0.12/€ 0.13/€ 0.12
On the next page: benchmarks, cache analysis and temperatures