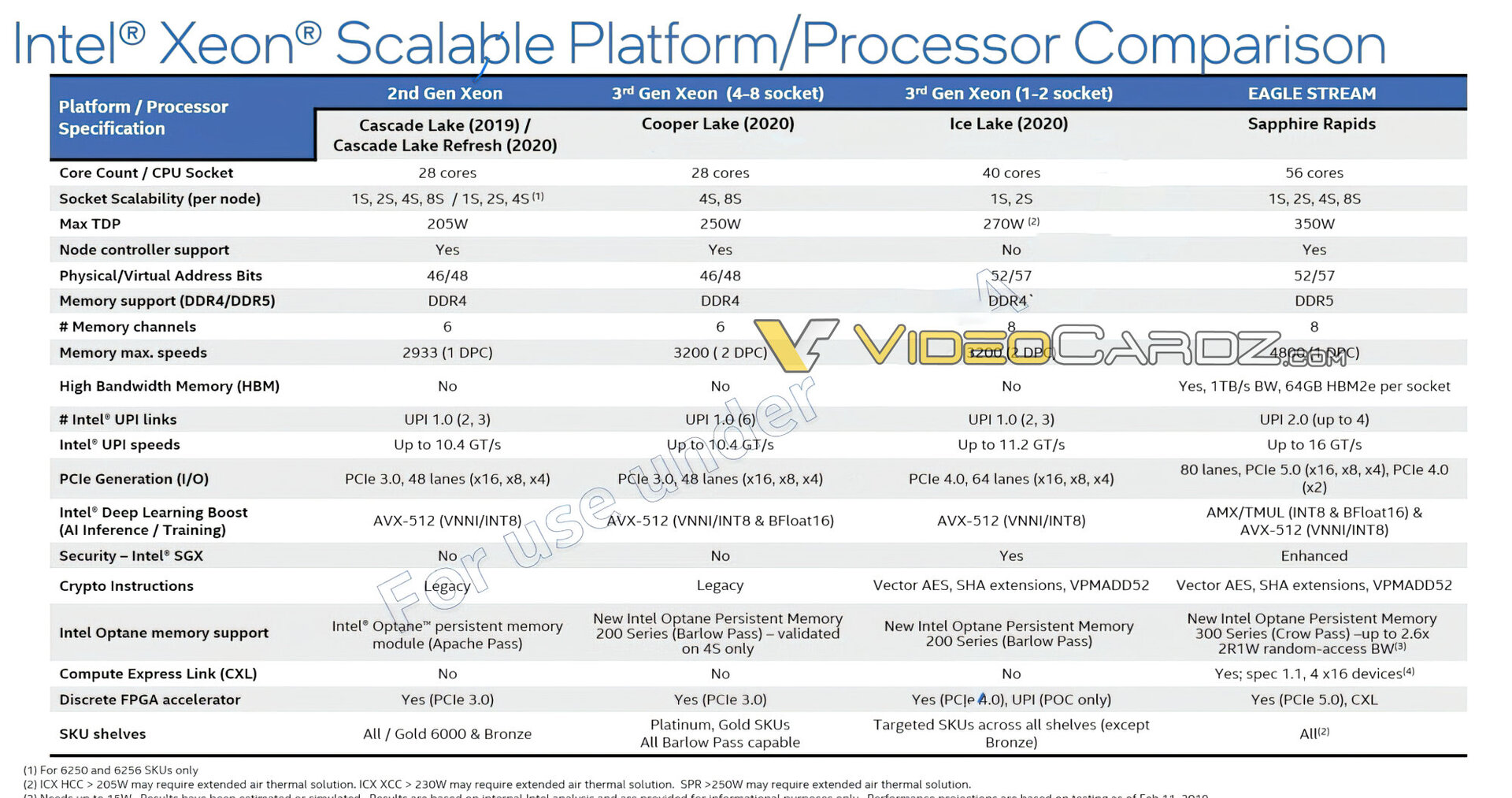
56 cores in the server, that was already available from Intel as a “glued” experimental CPU Cascade Lake-AP. With Sapphire Rapids, they should be acceptable for two to eight CPU sockets, in a smaller package and also with a lower TDP than with CXL-AP. A maximum of 350 watt TDP can also cover 64 GByte HBM2e in individual cases.
The TDP increases compared to Ice Lake-SP
Sapphire Rapids will again change the socket opposite Ice Lake-SP in the LGA 4189. The maximum TDP increases from 270 to 350 watts. However, TDP comparisons across generations and servers are always difficult. A large-area CPU can also dissipate more heat. Intel Cascade Lake-AP was able to achieve a TDP of 400 watts in the huge socket with 5,903 contact areas.
In terms of the dimensions of the complete package, however, Sapphire Rapids seems hardly or no larger than Ice Lake-SP, so that the TDP increase of up to 80 watts or 30 percent seems to be significant. HBM2e, like currently Optane Memory, should have its share in this. It is also questionable how large the share is due to CXL and PCIe 5.0 with even more lanes than before and ultimately has an impact on the TDP.
Multi-chip approach with four dies
Cascade Lake-AP was already a multi-chip CPU, but it was born out of necessity. Back then, two regular Xeons, each with 28 cores, were simply connected to one package via UPI. Cascade Lake-AP was basically a dual-socket CPU on only one package. Sapphire Rapids will implement the multi-chip approach differently. Instead of just two chips, four small CPUs with 15 cores each will be used. For reasons of yield, 14 of these will be used according to current information and thus form the 56-core CPU.
The UPI mentioned above will also be properly upgraded. Instead of the last steady typing steps with a minimal increase, UPI 2.0 will make the jump to 16 GT/s and be available with a maximum of 4 links. That should be necessary, as the new CPUs not only offer more cores, but also a lot more I/O and, above all, faster memory, be it apart from the package in the form of DDR5-4800 or very close to the CPU with HBM2e.
 Intel Xeon Sapphire Rapids (Image: Videocardz)
Intel Xeon Sapphire Rapids (Image: Videocardz) More PCIe lanes in 5th generation for the first time
80 PCI lanes per CPU are a step forward compared to Ice Lake-SP with 64 lanes, but ultimately the biggest innovation is PCI Express 5.0 instead of 4.0. It remains to be seen whether that will be enough compared to AMD. There have been 128 PCIe 4.0 lanes per CPU since Epyc 7002 “Rome”, of which, however, part of the communication between the CPUs is omitted in dual-socket operation. A maximum of 162 lanes are then effectively available at the end. But even that is already more on paper and will probably not be less in the next Genoa generation.
As is currently the case with Intel, the 56-core variant should mark the flagship, but the majority in the portfolio is below it. The multi-chip solution should allow a wide range of options for grading, whether with HBM or without it comes with it. A 44-core version and a variant with 24 cores were recently leaked. Since Sapphire Rapids is to replace both Ice Lake-SP for two-socket systems and Cooper Lake-SP for four- and eight-socket platforms, the portfolio of CPUs will be huge in the end.
🤔 pic.twitter.com/VRyGmMWQTB
& mdash; 188 号 (@momomo_us) April 6, 2021
Update 06/14/2021 07:37 am
Many new pictures show more details of the structure of the individual chips. In fact, 15 cores per die can be assumed, which amounts to the maximum expansion of 60 cores with four CPU chips per processor. For a better yield, one core is probably deactivated per die.
Update:
New pictures of SapphireRapids # intel #SapphireRapids pic.twitter.com/ibB53qiCF5& mdash;结 城 安 穗 -YuuKi_AnS (@AnsYuuki) June 12, 2021
Update : All modules # intel #SapphireRapids pic.twitter.com/KJa7mj5bNq
& mdash;结 城 安 穗 -YuuKi_AnS (@AnsYuuki) June 12, 2021

