The football is always dynamic, the risk of serious head injuries increases. For the new season, the Bundesliga makes a neurological Screening for all players is mandatory. But is this enough?
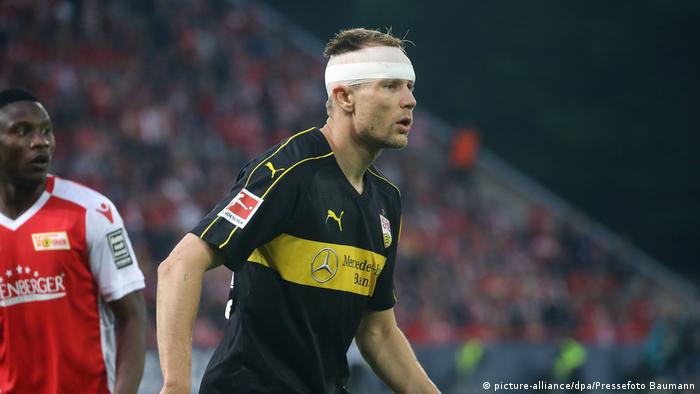
More games, or replace? The big question in the case of head injuries, such as in the case of Stuttgart, Holger Badstuber
“Put you feet one after the other so that they touch, lift the hands in the hips, and close your eyes. They now hold the balance for 20 seconds” – such commands are new for many of the Bundesliga players. A number of performance checks in the pre-season to the Routine, from this year, the club doctors need to put special attention to possible head injuries. The DFL requires all professionals to a so-called Baseline-Screening on the Basis of the SCAT-5 procedure. It is a comprehensive investigation, to conduct the in addition to the above-described balance test, a Check of other cognitive abilities, such as memory, reaction or spatial perception include. The investigation is time consuming, is to allow the Doctors in case of emergency, but to recognize a serious injury better.
“In a trend this is a good step,” says Daniela Golz of the society for sports neuro-psychology, “however, we will keep an agreed procedure, in addition to in-depth investigation is important.” Because the only way the injury and recovery could be assessed better.
DFL has drawn correct conclusions
Football is just one of the high-risk sports is Katrin Hemschemeier says. At the sports medical Institute, University of Paderborn, she conducts research with its working group for the Federal Institute for sports science: “In the Bundesliga we observe such violations nevertheless, on an almost weekly basis.” Cases like Stuttgart’s double-turban-makers, Holger Badstuber and Ozan Kabak in the Relegation or the Knock-out from Nuremberg’s goalkeeper Christian Mathenia in the headlines. The Keeper continued playing after a short period of unconsciousness. Also of Hanover, Noah Sarenren Bazee was released last November after a violent clash with Gladbach’s Matthias Ginter back on the court, before he fell a short time later due to severe Nausea and dizziness to the ground and was replaced. Later it was found a severe concussion.

K. o. after the collision: Nuremberg’s goalkeeper Mathenia played the match against Werder even to the end
“This is very critical,” says Werner Krutsch, Association physician of the Bavarian football Association, “the DFL has drawn the right conclusions from it.” In unison, the experts welcome the introduction of Screening. Also, because over the years a collection of data generated, the conclusions to be drawn on possible long-term consequences were possible, how Krutsch stressed.
UEFA calls for rule changes
To meet in case of an emergency on the course, the decision whether a player can continue, however, remains tricky. “As a Sideline Test, the Screening is not suitable,” notes Daniela Golz clearly, it would be too extensive. “You have three minutes, You need to use for simple Tests,” reports Werner Krutsch, too little for a proper diagnosis. Medical experience and knowledge of the player was as helpful.
In order to make the team easier for doctors, has stimulated the UEFA this year, the guardians of the world football Association Changes. In addition to the existing Three-minute break with a head injury, it could be an international Standard, that the managers of the stadium have by Tablet the possibility of the game scene in slow motion to look at. In the Bundesliga and the Premier League is already established.

If Bundesliga or Premier League, a player pushes the head, can look at the Doctors the slow motion
“This is a huge advantage, to the injury mechanism to better assess,” says Hemschemeier from my own experience, “from the distance from the side line of the is extremely difficult.” In addition, conceivable, but not yet in the discussion, would be the possibility of a temporary replacement of the player and the use of neutral Doctors.
Other Tests in development
The Bundesliga-Kicker benefit of the new Screening, when in a port of the game actually has a concussion or something worse is found. Because the Screening values can help, according to Hemschemeier and Krutsch accurate diagnosis, the recovery can be more easily monitored and controlled entry into the game better.
“A model for the American professional leagues NFL, NHL and NBA are in there,” explains Hemschemeier. “The have developed, in addition to the Baseline investigations, protocols [editors’ note: a sequence of certain testing] for the diagnosis and the “Return-to-Play” the players specifically for the respective sports. Since we have to go.” Further Tests, which could make the diagnosis in the next few years, sports-specific, faster and more accurate, are in the development stage. Some of these Tests are also suitable for performance diagnostics and training control and could lead to greater acceptance by coaches and players.