Hundreds of thousands of people die each year in Europe to air pollution, say epidemiologists. In some countries, it is to breathe more dangerous than others. That’s about to change, as for example in Poland.

“Smog is very tangible. You can see him you can smell him,” said Andrzej Gula, of the DW. “The people in Krakow joking, that one can bite him.” The kraków try to take it with Humor, even if the air pollution life may cost several Thousand people in Poland every year.
For Gula there are only two options, like you can with the filthy air deal: you either pulls away or becomes active. He has opted for the latter. For the past six years, he now fights with the citizens group of the Polish Smog Alert, the Polish Smog alert, air pollution in the second largest city in the country.
For many poles, the Check of the Smogwerte is now part of the everyday life, as well as the Wearing of respiratory protection masks. On some days, is recommended for children and older people to remain at home – outside, take a deep breath, then, is to dangerous. There may be headache, dizziness, and shortness of breath threatens not only the long-term effects, such as respiratory diseases and heart problems.
The worst time of the year in Poland. In Winter, the Smog increases dramatically, as a lot of people heating with the traditional wood and coal. In the winter months, the clothes, the people stink of Smog, says Gula. He compares the dirty air, the inhalation of people Smoking. Who lives in Krakow, and breathe each year, as many pollutants as if he would smoke to 3,000 cigarettes, appreciate activists.
Great A Health Hazard
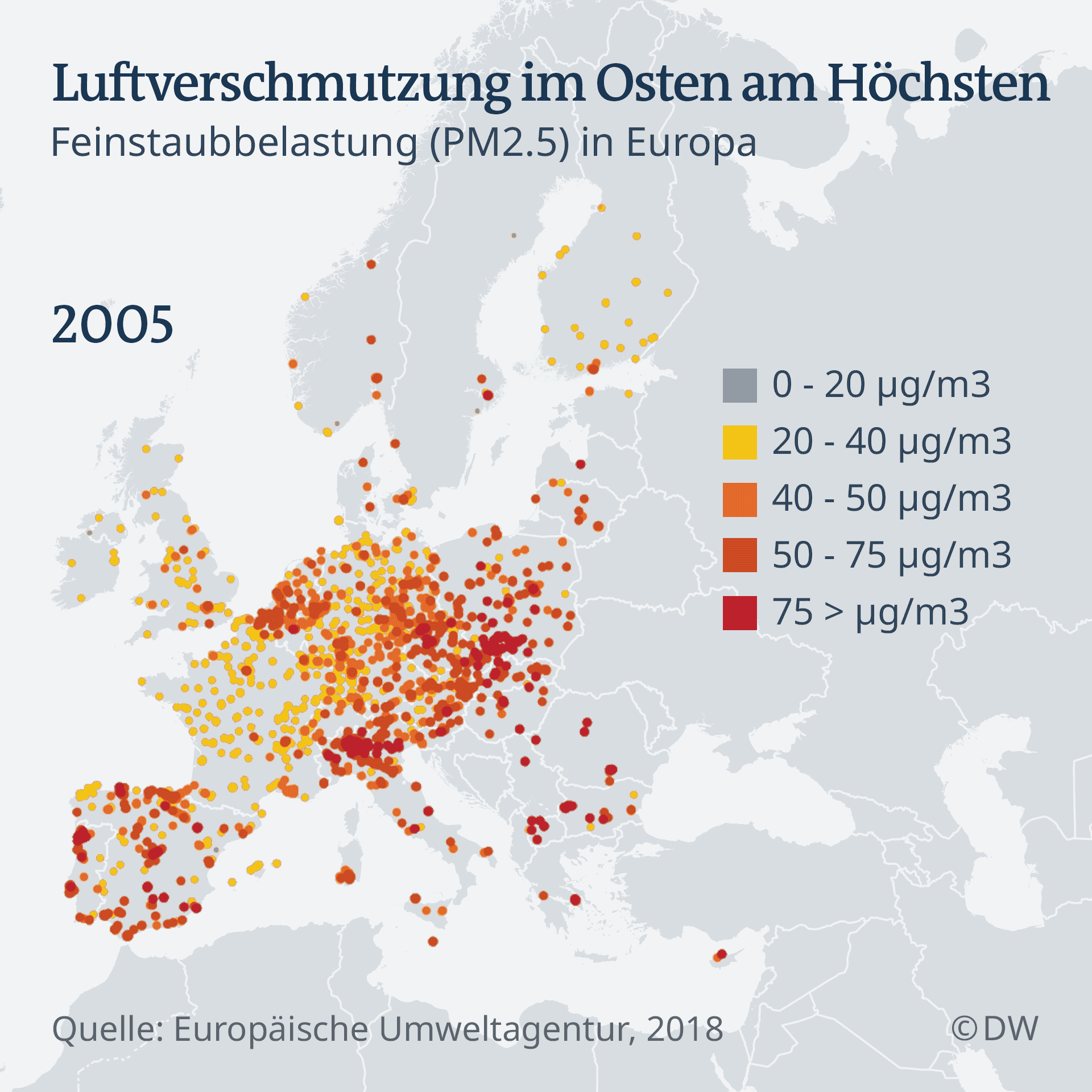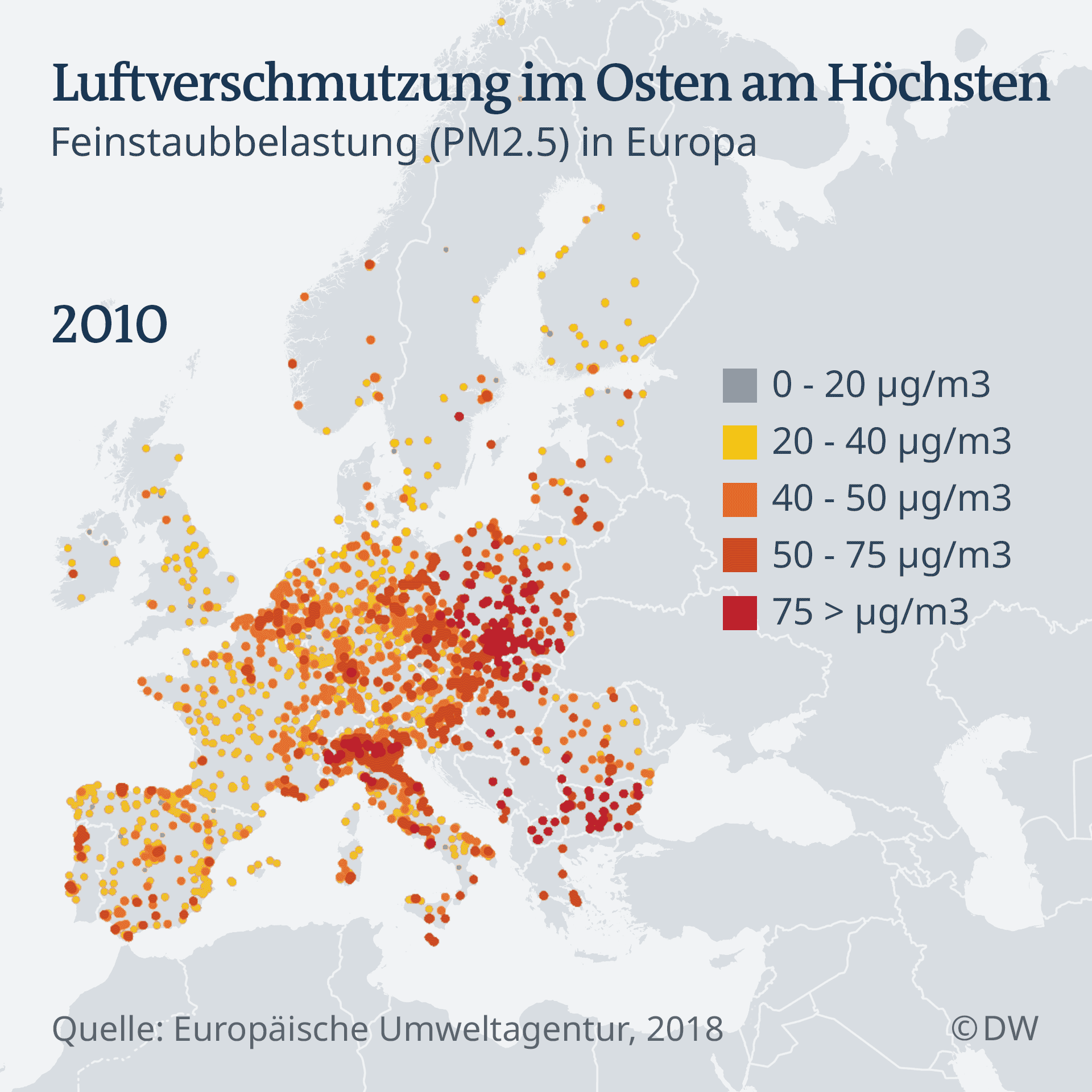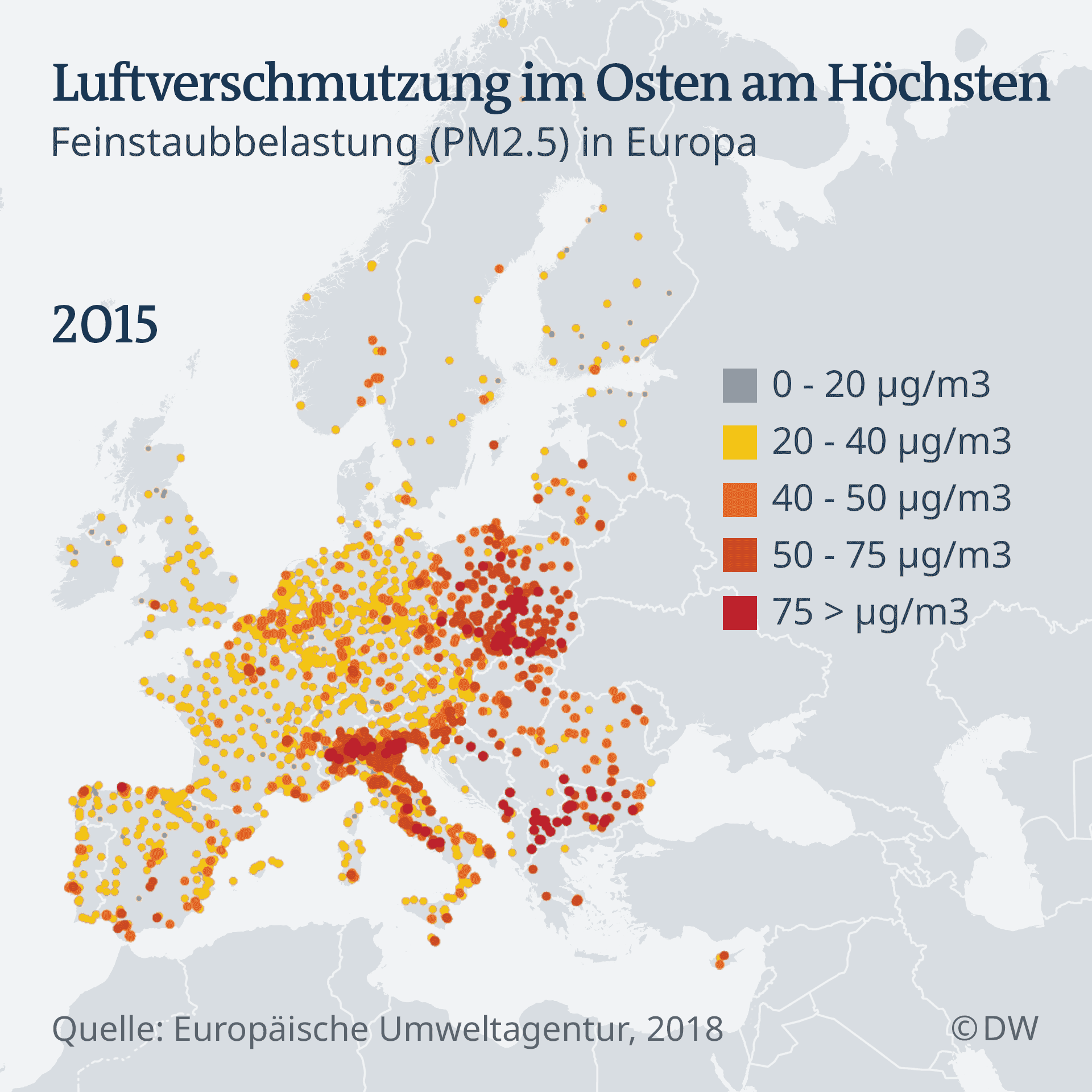
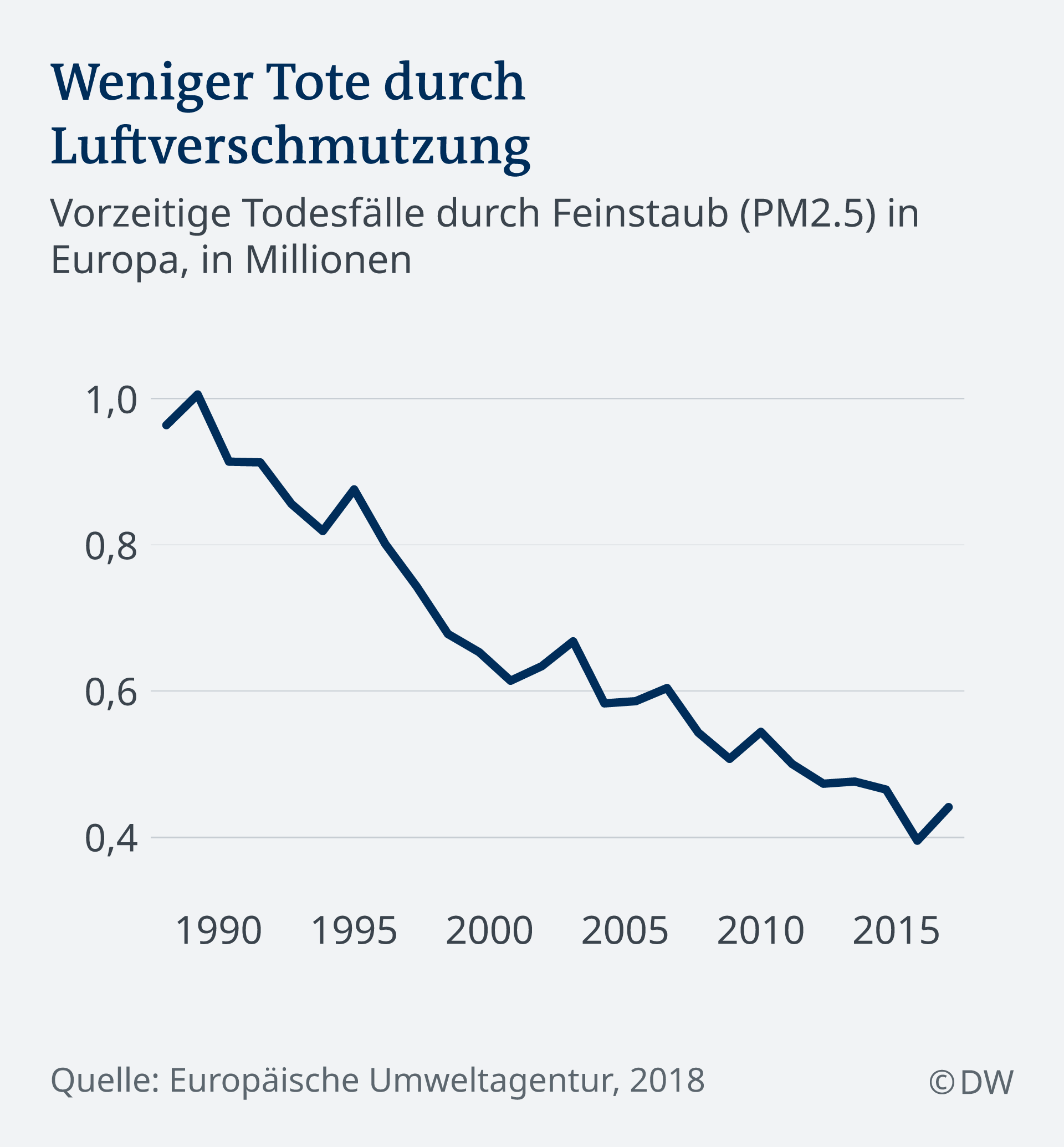
But the poles are not the only ones who have to fight with air pollution. Worldwide, billions of people breathe in every day toxic air. The world health organization (WHO) estimates that 7 million people in 2016, have died of air pollution. More than 90 percent of the children have to breath, therefore the toxic air. In Europe, by 2015, about half a Million people had died prematurely from the effects of air pollution, calculated by the European environment Agency (EEA).
An increased fine dust pollution is particularly dangerous for the health, since the microscope can penetrate small particles to the deep lung. Although the number of early deaths from pollution caused by air in the past three decades has steadily decreased, remain the pollutant values are still dangerous and illegal. It is already much better than in the past: in 1990, high pollutant loads were almost twice as many deaths as it is today. But still, around 90 percent of Europeans living in cities, the health breathing in harmful air, the sea. Air pollution remains the biggest threat to health in Europe.
In the air, more pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides, ozone, and ammonia, emitted by industry, road transport, agriculture and the heaters out in addition to fine dust. While in almost all areas, pollutants have been reduced, the ammonia emissions in agriculture. About Alberto González of the European environment Agency are particularly concerned. Because, if the gaseous ammonia enters the atmosphere with other pollutants from vehicle exhaust gases reacts, a new fine dust, the deadliest pollutant for humans.
Around 94 percent of the ammonia emissions in the European Union in the agriculture sector, in particular in animal husbandry. In agriculture have taken place since 1990, no major emissions reductions. “It is very important that we are finally active in agriculture, to fight against the air pollution,” said González of the DW.
Where in Europe is it to breathe?
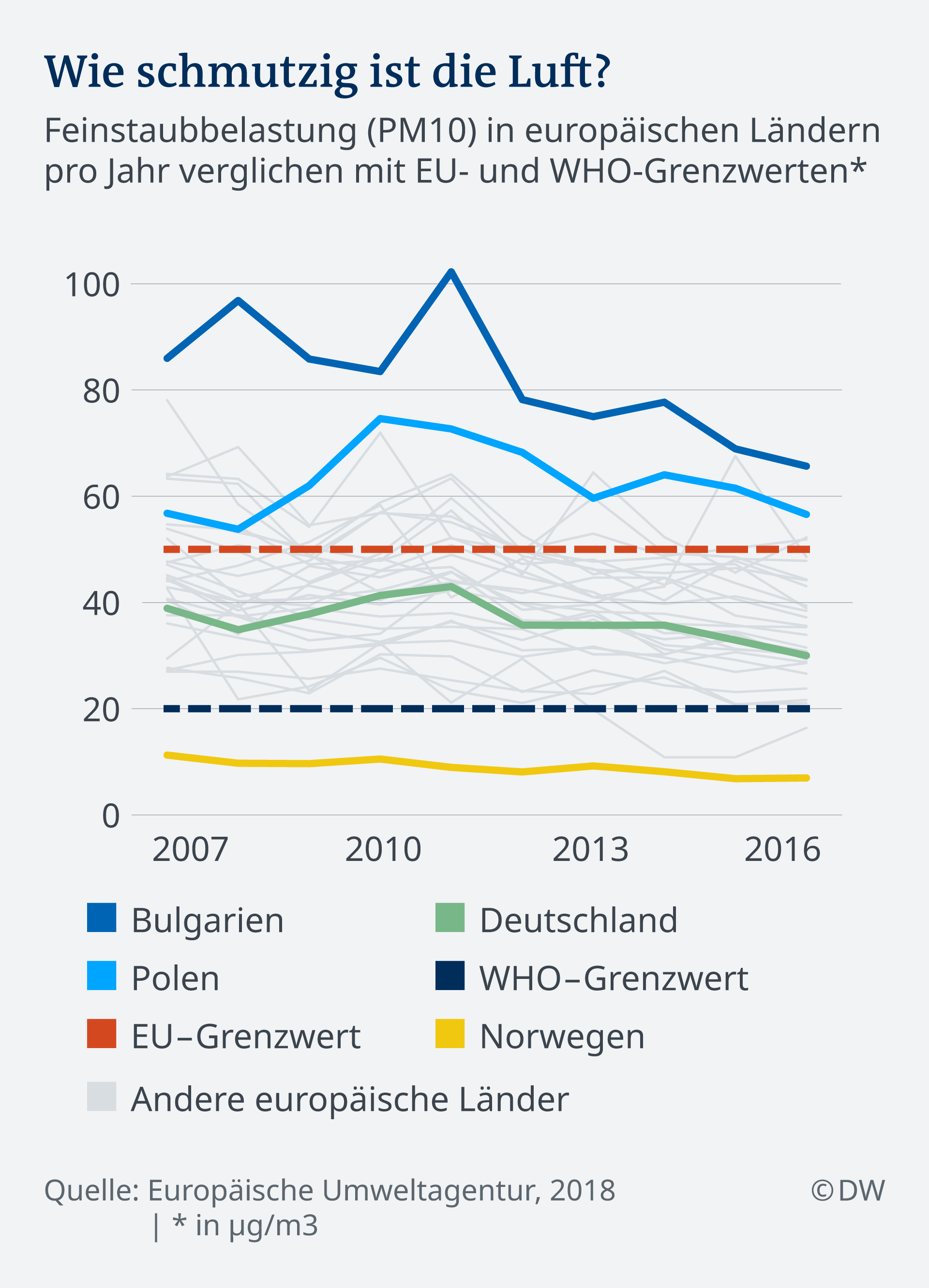
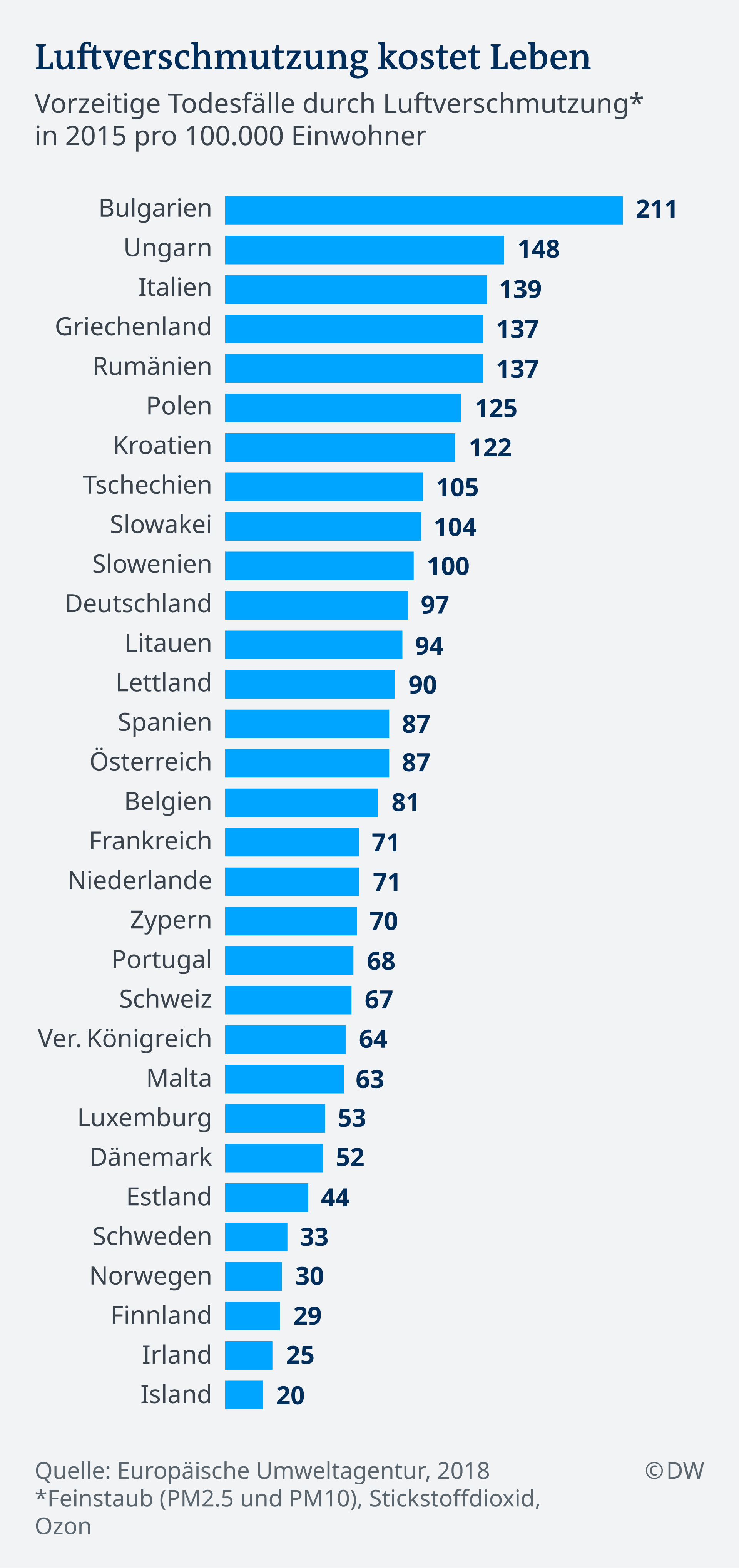
Not everywhere in Europe, the air is equally bad. Generally, the pollutant levels in Central and Eastern Europe is higher than in the Rest of the EU. Bulgaria has the worst air quality and most early death is one of the cases due to air pollution. Reason for this is mainly particulate matter emissions from heaters, González says.
More deaths due to pollution here: caution in epidemiological studies
and here: epidemiologist: deaths are estimated
Poland, hosts of this year’s climate change conference in December, following Bulgaria in the list of European countries with the worst air quality. Air pollution kills around 45,000 people each year in Poland, experts estimate. According to the WHO, 33 of the 50 dirtiest cities in Europe in the last year in Poland. One of these cities of Katowice, where the climate conference will take place. In Poland, coal – and wood-fired heaters of the main causes for the Smog and fine dust emissions.
Germany ranges in the middle. When all data are combined, the Federal Republic of Germany, the annual EU limit values for fine dust. But especially in cities the air is often significantly worse. In Stuttgart, for example 64,40 micro-fine grams of dust per cubic meter of air is measured, the legal limit is 50 micrograms.
Norway is the only country in the EU, in the air is even consistently cleaner than required by the WHO, the stricter limit values than the EU. Norway’s green strategy, such as the promotion of clean vehicles, pays for itself.
Poland will exchange dirty heaters
In some countries, the realization of how dangerous pollutant-Laden air is growing in the population. Also in Poland the issue of air pollution is making more and more headlines, thanks to campaigns from activists such as Gula in Krakow. At the same time pressure from the EU has helped to rethink, says Przemyslaw Hofman, head of the Department in the area of low-emission economy in Poland Ministry of entrepreneurship and technology.
The Polish government now wants to do something for better air and has not banned the sale of heating baths, which conform to the emission standards. For this, they provides 25 billion euros within the next ten years, so that poorer residents will be able to exchange your old heaters with newer, cleaner heating systems.
Regional governments are already a step further. In Krakow, most of the coal heaters were replaced by lower-emission Alternatives such as gas heaters. Krakow will soon ban as the first city in Poland the use of wood and coal completely.
At the EU level, a package of measures for clean air in 2013 for improvement. By 2030, air pollution will be reduced significantly and the number of premature deaths can be halved. This is only possible if all countries keep to the targets. After that, it is not, however, in many member States at the moment. In may, the EU has sued the Commission, Germany, France, UK, Italy, Hungary and Romania because of bad air in the cities.
Irene Banos, Ruiz travel costs to Poland were taken over by Clean Energy Wire and Forum Energii.