A group of American researchers has memristors, resistors with memory, developed in water can work. This can pave the way for integration in the body. Memristors are relatively new elektronicabouwstenen.
Memristors were already in 1971 mentioned as possible elektronicacomponent. After resistors, capacitors and inductors they would be the fourth passive component. Only in 2008 did researchers from HP Labs managed to they actually produce. Just like other electrical components, such as resistors and capacitors, memristors, memory resistors or geheugenweerstanden called, out of traditional materials. A group of scientists from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at North Carolina State University has, however, gel-based, biocompatible memristors developed.
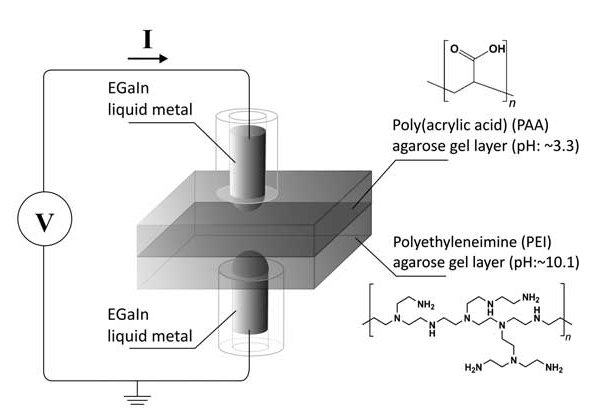
The prototypes were made from hydrogels of agarose used, that of polyëlektrolyten were equipped with two electrodes to connect the gels. In place of electron transport, as with regular electronic components, use the gels, ion transport. The gels can in an aqueous environment to function, so that they, for example, in biocompatible implants may be used. The researchers think the use of memristors as artificial neurons that live neurons can be connected.
The research team developed previously, photovoltaic cells, diodes and other electrical components on the basis of his gels. That made use of metal electrodes that are rigid. The new memristors are using electrodes of a liquid metal, where the metal layer an oxide is formed which is essential for the operation as a memristor. The thickness of the oxide layer determines the resistance of the memristors and the two gellagen have different resistances by the choice of the electrolytes.
The research group focuses its ‘soft matter’research on sensors and actuators. Combined, that would in the long term can lead to ‘soft robotics’ or on gel-based robots that are biologically degradable and natural movement. Also would the memristors as a neuronal synapse can be used, which simulate brain and the connection of artificial with biological neurons.